The Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology has implemented substantial measures to advance the utilization of sustainable and renewable energy throughout the campus. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) underscore the necessity for universal access to affordable, sustainable and modern energy, prioritizing the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions and the promotion of renewable energy sources. It underscores the expansion of renewable energy, improvements in energy efficiency, and the adoption of environmentally friendly technology in both developing and developed regions. The major purpose is to deliver electricity and clean cooking solutions to marginalized rural and isolated populations, achieved through a transition to renewable energy sources like as solar, wind, and hydropower to reduce emissions and address climate change.
Institutional Pathways to Energy Optimization
Our institution has undertaken a series of impactful alternate energy source initiatives to advance sustainability and clean energy. Through renewable energy installations such as solar panels, wind energy projects and biogas plants, it is actively reducing dependence on conventional power sources. Solar photovoltaic panels, solar thermal systems and small-scale windmills are included into the design of all newly built buildings, lowering dependency on the grid and providing clean electricity for laboratory operations and illumination. Complementing this, energy efficiency measures including smart lighting systems, regular energy audits, and the development of green buildings ensure optimal resource utilization and reduced environmental footprint. At the governance level, the establishment of an institutional energy policy, a dedicated sustainability cell, and strategic collaborations further strengthen the framework for long-term energy management and eco-conscious growth.
The Institution is actively engaged in the advancement of various solar cell technologies within the realm of research and innovation. These encompass thin-film solar cells, silicon-based photovoltaic modules, perovskite solar cells, and heterojunction oxide solar cells. Our institution has,
10 kW rooftop solar panels powering pavements and laboratories
Solar-powered kitchen recommissioned, reducing LPG usage
Solar lamps installed along walkways
Research on third-generation solar cells to power battery-operated vehicles.
Solar Panels on rooftop


Solar panels on top of pathway Shelters with controller

Hybrid Wind Solar System
Sathyabama has established a solar-wind hybrid system to enhance its renewable energy framework, providing stable and continuous power to multiple scientific facilities while alleviating the burden on the conventional grid.


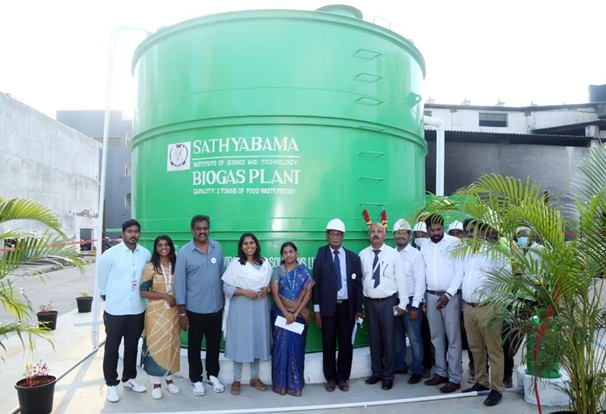
The Institution manages biogas systems that transform organic waste into fuel for cooking in the hostel mess. The biogas plant in our institution has
20 L capacity demonstration unit using food waste.
Biogas used to replace approximately three LPG cylinders/day in kitchens.
Research on microbial fuel cells (MFC) for electricity generation from food waste.

Biodiesel
Biodiesel Plant for the usage in Institutional buses and Gensets. The institution operates a pilot scale biodiesel production unit that converts 50 litres of waste cooking oil generated in the institution mess. This initiative prevents approximately 15,000 to 20,000 Litres of waste cooking oil from being consumed, thrown into the sewer line or dumped onto the landfill every year. The waste cooking oil is properly assessed and converted into Biodiesel.
The produced biodiesel is evaluated to meet the ASTM standards. Fifteen of the institution buses are operated with B15 blends of diesel. Also, two of the Gensets are powered with B-100. With this initiative the institution has reduced 4,82,460 TCO2E from 37,84,000 TCO2E per annum by operating biodiesel powered buses and gensets which is 33,01,540 TCO2E . The institution has set it’s target to achieve 50 percent by increasing the blending percentage as well as the number of biodiesel powered buses. The scope for the institution to reduce emissions is huge and will be achieved as set by the nation.
Biodiesel Production Unit at CWM, Sathyabama

LED bulbs/ Power Efficient Equipment
Institution Initiatives for Carbon Reduction
Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology has undertaken extensive plantation drives across its campus to strengthen its commitment to sustainability and carbon reduction. The institution recognizes the vital role of flora in absorbing carbon dioxide and improving air quality, and therefore maintains a diverse green cover that includes matured trees, semi‑grown trees, and a wide variety of bushes. In order to reduce the direct emissions on campus, the management has launched the battery cars for on campus transportation of students, staff and guests.


Research and Innovation in Clean Energy Technology
Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology has established multiple dedicated research centres to encourage advanced Research and Development activities in innovative technologies that foster a cleaner and greener environment.
Centre of Excellence for Energy Research

The Centre of Excellence for Energy Research (CEER) at Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology was established under the MHRD’s Frontier Areas of Science and Technology (FAST) scheme and inaugurated on December 9, 2014, by Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, Former President of India, in the presence of Col. Dr. Jeppiaar, Founder Chancellor. CEER serves as a premier hub for sustainable energy technologies, focusing on advanced research in solar photovoltaics, fuel cells, supercapacitors, batteries, electrocatalysis, thermoelectric devices, and bioenergy. With state-of-the-art infrastructure and expert faculty, the centre bridges academic innovation and industrial application, fostering product development and technology transfer. The vision of the centre is to be a global leader in transformative energy research, driving sustainable innovation and shaping the future of clean and efficient energy technologies for societal and environmental betterment. Through interdisciplinary collaboration with academia, industry, and government bodies, CEER promotes impactful solutions for affordable and clean energy, while also advancing knowledge dissemination and capacity-building programs that strengthen global energy security and contribute to long-term sustainability.
https://centreforenergyresearch.com/index.html
Centre for Waste Management

In collaboration with the National Solid Waste Association of India (NSWAI), Sathyabama established the Centre for Waste Management (CWM) in 2011. Since its inception, the Centre has become a hub for waste-to-energy research and innovation, focusing on converting food waste, plastics, ritual waste, biomedical waste, and e-waste into valuable resources such as biogas, biodiesel, activated carbon, microbial fuel cells, and sustainable building materials.
The Centre’s work includes developing patentable technologies, publishing in peer-reviewed journals, training graduate students, and offering consultancy services. Beyond research, it actively engages in public awareness campaigns on waste segregation and recycling, ensuring that scientific outcomes are transferred for societal benefit. By integrating the 3R principles—Reduce, Reuse, Recycle— into its mission, the Centre exemplifies how waste can be transformed into clean energy, thereby reducing carbon footprints and promoting a circular economy.
https://www.centreforwastemanagement.com/index.htm
Important Links of the Energy Research Activities
Publications:
https://centreforenergyresearch.com/publications.html
Outreach and Community Engagement Programs on Clean Energy
Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, through its Centre for Waste Management (CWM) and the Science Technology & Innovation Hub (STI-Hub), runs the Village Program to promote scientific and technological interventions for the socio-economic development of local communities
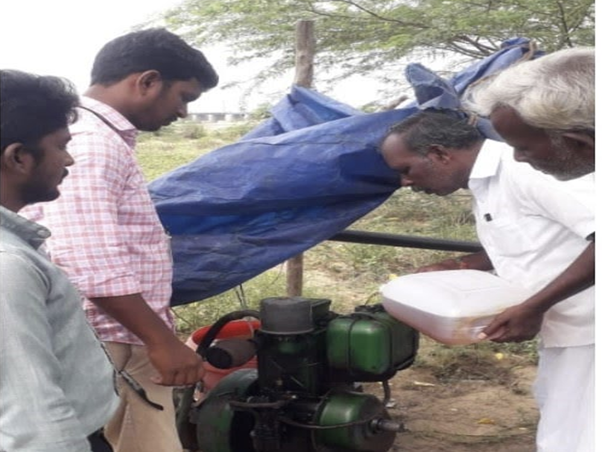
Biodiesel for pump sets and gensets in Mittapalli, Aadhanur, Eachampoondi, Meensuruti villages Apart from directly contributing, the institution through its biofuel promotion activities has also contributed to Carbon footprint reductions. About 5300 L of biodiesel has been given away for operating pump sets in Mitapalli village, Aadhanur village, Eachampoondi village in Tamil Nadu. The institution is also taking initiatives to provide biodiesel to power fish catching boats in Meensuruti village in Kattumannarkoil Taluk, Cuddalore district. In addition to the biodiesel plant commissioned in the Centre for Waste management Laboratory at Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, a pilot scale biodiesel plant has been set up in Cuddalore to cater to the diesel requirements in few of the villages in Kattumannarkoil Taluk. This way 2.14 TCO2E has been achieved indirectly by the initiatives taken by our institution during 2023-2024, which would have been high with diesel used as a fuel. The target will be to increase in cumulative reduction of 5, 10,15,20 tonne year after year in next four years and achieve a total of 55 TCO2E by 2028. Through the Science Technology and Innovation hub established at Kattumannarkoil Taluk C, D block Cuddalore District around 150 marginal and non-workers including women have been trained to make biodiesel from waste cooking oil. They are given sufficient awareness on the impact of consuming several times fried waste cooking oil and throwing away of the same on landfills and into the sewer lines. They have been trained to check the quality of the oil, categorize it for biodiesel production, divert it for other application like detergent soap making, 1 Litre biodiesel production and 20 L pilot scale biodiesel production.

Biodiesel Plant housed in Eachampoondi Village, Cuddalore District in the STI Hub, a DST-Sathyabama Joint initiative


Our institution’s Fly ash brick manufacturing workshops promoted eco-friendly construction materials, reducing reliance on traditional clay bricks. Hydroponics training introduced farmers to water-efficient farming methods, addressing challenges of water scarcity.

Workshops and Training Programs on Renewable Energy
Centre for Waste Management, Centre of Excellence for Energy Research jointly with Centre for Aquaculture Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology organizes Biodiesel production and Characterization training. Participants in this project, many of whom were from institutions and enterprises in Chennai and other regions of India, were able to comprehend realistic strategies for implementing decentralized waste-to-energy systems. Through live demonstrations at the campus biogas plant, participants received practical instruction in anaerobic digestion, food waste processing, biogas scrubbing, and clean fuel utilization.
The institute offers advanced scientific instruction related to energy materials and characterisation. The Training Program on Advanced Characterization Techniques (June 23–24, 2023) is one of the major programs. It introduced participants to sophisticated spectroscopy and microscopy instruments that are necessary for evaluating materials used in energy devices.


Researchers and industry professionals were introduced to state-of-the-art solar materials, hydrogen energy systems, battery technologies, and supercapacitors during the Five-Day FDP on Advanced Materials for Energy Applications (October 9–13, 2023).

Important Links
Publications
https://centreforenergyresearch.com/publications.html
Startup
ChemMatNano Pvt Ltd. | Nanomaterials and Perovskites | India
Collaborations and MoUs
MoU with WasmanPro Environmental Solutions LLP, Chennai
Date: July 2023
Focus: Diverting food waste to biogas units, reducing LPG consumption in institutional kitchens.
MoU with NIN Energy India Pvt Ltd
Date: November 2023
Focus: Conducting professional energy, environment, and green audits for the campus.
Other MoU and Collaborations on Clean Energy
Central Leather Research Institute (CLRI) – Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil.
Science, Technology, and Innovation Hub (Cuddalore) – Training 150+ rural workers, including women, in biodiesel and bio-compost production.
Our institution also holds MoU with foreign universities in Europe and Asia working on solar photovoltaics, hydrogen production, and energy storage focusing on faculty/student exchange programs, joint research publications, and collaborative projects in clean energy.
International Collaborations via CEER – Joint projects on solar cells, fuel cells, and hydrogen production with global universities.







